Firebase Realtime Database is a cloud-hosted database that helps us to store and sync data with NoSQL database in realtime to every connected client platforms like Android, iOS, and Web.
Nowadays NoSQL databases are gaining popularity and Firebase Realtime Database is one of the NoSQL databases. Firebase store all the data in JSON format and any changes in data reflects immediately by performing a sync operation across all the platforms. This allows us to build a flexible realtime app easily with minimal efforts.
Firebase Realtime Database feature
In this post, we'll see the basics integration of Firebase realtime database and build a Flutter App that allows us to perform the CRUD operations with Firebase Database in a ListView. The final output of the example look like above video.
If you are new to Firebase, I suggest you read our other post about Firebase configuration and Firebase Auth to improve your knowledge. On the basis of the previous post, we assuming you have configured Flutter app with Firebase console.
Before dive into the application development, i would like to give you basic information about performing CRUD operations and other aspects of the realtime database. Later we’ll combine all these concepts together to build a simple app with Firebase realtime database as back-end.
How data store on Firebase cloud?
As we know, the Firebase realtime database is a schema-less and NoSQL based database. We can store the entire database in a big JSON tree with multiple nodes format. So, before start application development. We need to prepare the JSON structure in a way that the data is accessible in an easier way by avoiding nesting of child nodes. As you can see below, we have prepared a structure for this example application. We storing a list of user profiles and user count in the JSON tree.
How can enable offline persistence in Flutter?
Firebase provides great support when your application in offline mode. It automatically stores the data offline when there is no internet connection. When the device connects to the internet, all the data will be pushed to the realtime database. Disk persistence can be enabled by calling below code.
How can manage Security & Rules?
Firebase provides a great way to make database secure. We can apply a way to identify user role while performing read and write operations. These rules will acts a security layer on the server before perform any CRUD operation. Let's check it.
1. The below rules allow authenticated users can perform read or write operation.
2. Below rules allow everyone can read & write data without authentication. We'll use it in the demo app.
3. You can also use the following rules to validate data before inserting into the database. You can validate the name to be less than 50 chars and email to be valid using email regular expression.
How can perform CRUD Operations?
To perform any operation on to database whether it can be read or write, you need to get the reference of database node. The below code gives you reference to database JSON top node. From here you need to use the child node names to traverse further.
Inserting Data
To insert data, you can use set(key, value) method on to database reference path. This will create the value on the path provided to a given reference. As you can see below, we inserting a user information to user reference node.
Reading Data
To read the data, we can use FirebaseAnimatedList widget of Firebase database plugin. In which, we pass the root reference of a node in the query parameter. This event will be triggered whenever there is a change in data in realtime. As you can see below, as each parameter define its feature. In the itemBuilder parameter, we'll get the actual value of an item.
Updating Data
To update data, you can use the update(key, value) method by passing the new value.
Deleting Data
To delete data, you can simply call remove() method on to database reference.
Now we have enough knowledge to get started with a Flutter application. Let’s create one and see how to integrate the realtime database with an example app. Below are the steps you need to follow to set up your project for using Firebase realtime database.
Creating a new Project
1. Create a new project from File ⇒ New Flutter Project with your development IDE.
2. Now, configure your application with Firebase cloud. As explained here.
3. Open pubspec.yaml file and add firebase_database: ^1.0.5 dependency.
4. Open main.dart file and edit it. As we have set our theme and change debug banner property of Application.
5. After that create a user.dart file. It is a POJO model that'll contain user information.
6. For code simplicity, i have created a separate file firebase_database_util.dart. Here, i have written all CRUD methods that we'll use to interact with firebase database. Before calling any method of this util. We have to call the initState method to initialize it.
7. Now start the development of user interface. To display a list of the user, we have created another file user_dashboard.dart. To understand it deeply, we have written the doc in yellow color of each snippet in this file. So, read it carefully to the better understanding of the following widget.
The output of the above widget looks like below when you'll run this project.
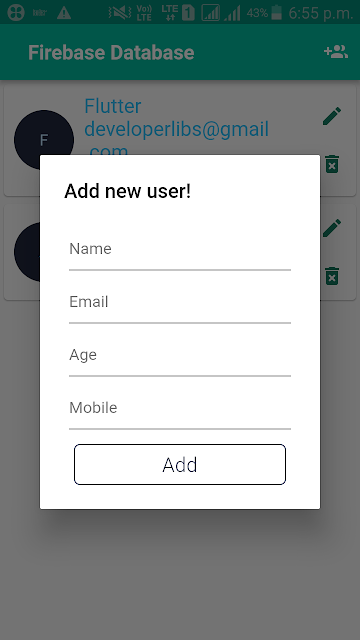
8. Let's see final code snippet of this project. We are going to create a pop-up widget. It will show user info entry fields. When we add and update user info.
The final output of the above widget looks like below.
If you have followed the article carefully, you can see the app running very smoothly as shown in the above video. But if you are facing any problem or you have any quires, please feel free to ask it from below comment section and you can ask it on SLACK.
Firebase Realtime Database feature
- Realtime: – It means the data is synchronized with all connected devices within milliseconds of changes being made to the data.
- Offline: - The Firebase Realtime Database persists data on your device. The data is always available, even app offline. The data is automatically synced once the app comes back online.
- Security: – You can define your security rules which controls who has what access to your Firebase database. You can also integrate Firebase Authentication to control access to your data.
In this post, we'll see the basics integration of Firebase realtime database and build a Flutter App that allows us to perform the CRUD operations with Firebase Database in a ListView. The final output of the example look like above video.
If you are new to Firebase, I suggest you read our other post about Firebase configuration and Firebase Auth to improve your knowledge. On the basis of the previous post, we assuming you have configured Flutter app with Firebase console.
Before dive into the application development, i would like to give you basic information about performing CRUD operations and other aspects of the realtime database. Later we’ll combine all these concepts together to build a simple app with Firebase realtime database as back-end.
How data store on Firebase cloud?
As we know, the Firebase realtime database is a schema-less and NoSQL based database. We can store the entire database in a big JSON tree with multiple nodes format. So, before start application development. We need to prepare the JSON structure in a way that the data is accessible in an easier way by avoiding nesting of child nodes. As you can see below, we have prepared a structure for this example application. We storing a list of user profiles and user count in the JSON tree.
How can enable offline persistence in Flutter?
Firebase provides great support when your application in offline mode. It automatically stores the data offline when there is no internet connection. When the device connects to the internet, all the data will be pushed to the realtime database. Disk persistence can be enabled by calling below code.
How can manage Security & Rules?
Firebase provides a great way to make database secure. We can apply a way to identify user role while performing read and write operations. These rules will acts a security layer on the server before perform any CRUD operation. Let's check it.
1. The below rules allow authenticated users can perform read or write operation.
2. Below rules allow everyone can read & write data without authentication. We'll use it in the demo app.
3. You can also use the following rules to validate data before inserting into the database. You can validate the name to be less than 50 chars and email to be valid using email regular expression.
How can perform CRUD Operations?
To perform any operation on to database whether it can be read or write, you need to get the reference of database node. The below code gives you reference to database JSON top node. From here you need to use the child node names to traverse further.
Inserting Data
To insert data, you can use set(key, value) method on to database reference path. This will create the value on the path provided to a given reference. As you can see below, we inserting a user information to user reference node.
Reading Data
To read the data, we can use FirebaseAnimatedList widget of Firebase database plugin. In which, we pass the root reference of a node in the query parameter. This event will be triggered whenever there is a change in data in realtime. As you can see below, as each parameter define its feature. In the itemBuilder parameter, we'll get the actual value of an item.
Updating Data
To update data, you can use the update(key, value) method by passing the new value.
Deleting Data
To delete data, you can simply call remove() method on to database reference.
Now we have enough knowledge to get started with a Flutter application. Let’s create one and see how to integrate the realtime database with an example app. Below are the steps you need to follow to set up your project for using Firebase realtime database.
Creating a new Project
1. Create a new project from File ⇒ New Flutter Project with your development IDE.
2. Now, configure your application with Firebase cloud. As explained here.
3. Open pubspec.yaml file and add firebase_database: ^1.0.5 dependency.
4. Open main.dart file and edit it. As we have set our theme and change debug banner property of Application.
5. After that create a user.dart file. It is a POJO model that'll contain user information.
6. For code simplicity, i have created a separate file firebase_database_util.dart. Here, i have written all CRUD methods that we'll use to interact with firebase database. Before calling any method of this util. We have to call the initState method to initialize it.
7. Now start the development of user interface. To display a list of the user, we have created another file user_dashboard.dart. To understand it deeply, we have written the doc in yellow color of each snippet in this file. So, read it carefully to the better understanding of the following widget.
The output of the above widget looks like below when you'll run this project.
8. Let's see final code snippet of this project. We are going to create a pop-up widget. It will show user info entry fields. When we add and update user info.
The final output of the above widget looks like below.
If you have followed the article carefully, you can see the app running very smoothly as shown in the above video. But if you are facing any problem or you have any quires, please feel free to ask it from below comment section and you can ask it on SLACK.